Budgeting Projects
Budgeting Projects
Plan cost management – “the process that establishes the policies,
procedures, and documentation for planning, managing, expending,
and controlling project costs.” PMBOK® Guide
Cost management plan – “a component of the project
plan planned structured
that describes how costs will be planned, structured,
and controlled.” PMBOK® Guide
Purposes of the Cost
Management Plan
- How to develop and share relevant, accurate and timely information for decision making
- Provides feedback linking the project to business objectives
- Provides detail and summary information
- Helps project stakeholders focus on schedule performance and cos
Estimate Cost
Cost estimating - “the process of developing an approximation of the cost of the resources needed to complete project activities ”.
accuracy of cost
estimates
|
|
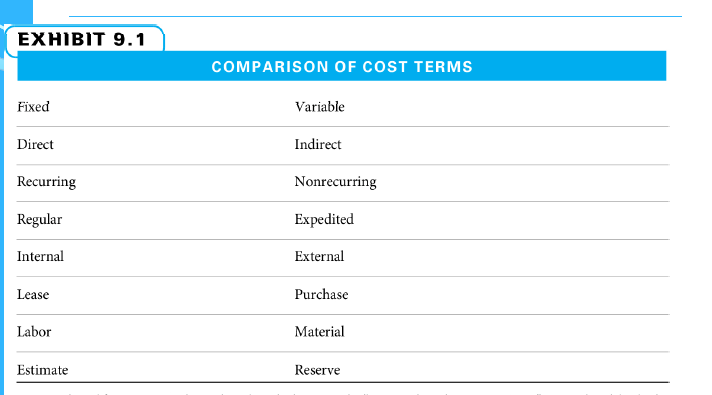
Types of Costs
Fixed vs. Variable Cost
Project cost and volume
curve
Direct vs. Indirect Costs
Direct Versus Indirect Costs
Recurring vs. Nonrecurring
Costs
Recurring costs repeat as the project
work continues
◦ Cost of writing code; laying bricks
◦ Occur during project execution
Nonrecurring costs happen only once
during a project
◦ Design development
◦ Occur during project planning and closing
Regular vs. Expedited Costs
Regular costs occur when progress
can be made by normal work hours
and purchasing agreements
◦ - the preferred cost
Expedited costs occur when the
project must be conducted faster than
normal
◦ Overtime and extra charge apply
Estimate vs. Reserve Costs
Project estimates need to be
aggressive
Add a reserve to cover activities that
run over aggressive estimates
Estimate – “a quantified assessment of the likely amount…It should
always include an indication of accuracy.”
Reserve – “a provision in the project management plan to
mitigate and/or risk cost schedule risk. Often used with a modifier
(e.g. management reserve, contingency reserve) to provide
further detail on what types of risk are meant to be mitigated.
Management reserve – “an amount of the project budget withheld
for Management control purposes … for unforeseen work that is within the scope.” PMBOK® Guide
Contingency reserve – “a provision in the project budget within the cost baseline that is allocated for identified risks that are accepted and for which contingent or mitigating responses are developed.
Accuracy and Timing of Cost
Estimates
Order of Magnitude Estimates
Created when limited project detail is available
Enough information for “go” or “no
go” decision
Budget and Definitive
Estimates
More accurate cost estimates at
each stage
Rolling wave planning
◦ Definitive estimate for the 1st stage
◦ Order of magnitude for the remainder
Methods of estimating costs
Analogous estimating
Parametric estimating
Bottom-up estimating
Analogous Estimating
A similar project --->a starting point
Experience performing similar
projects
Actual costs of similar projects
Knowledge of how project differs
Experience with methods used to
perform the project
Analogous estimating – “a technique for estimating the duration or cost of an activity or a project using historical data from a similar project.
Parametric Estimating
Involves finding more information
regarding the project
Parametric estimating – “an estimating technique in
which an algorithm is used to calculate cost or
Duration based on historical data and project
parameters.
Bottom-Up Estimating
Most detailed – specifications need to
be very clear
Time consuming
Most accurate form of estimating
Ensure every item is included
Bottom-up estimating - “method of estimating project
duration or cost by aggregating the estimates of the lower-level
components of the WBS.”
Cost Estimating Method
Comparison
Project Cost Estimating Issues
Supporting Detail
Scope
Method used
Version control is critical
Assumptions
Constraints
Different assumptions by different people
Range of possible outcomes
Untrue assumptions cause more work
Direct Labor Assumptions
Workers will be paid at the prevailing wage
rate of $14 per hour
Workers are already familiar in general
with the technology being used on the
project
Workers will be paid for 40 hours per week
whether there is always that much work for
them or not
Overtime will never be authorized
The project schedule can be delayed if the only alternative is to pay overtime.
Supporting Detail - Constraints
Only in-house workers will be used
No extra space will be provided
No extra budget will be allowed
The current version of the XYZ software will be incorporated into the design.
Causes of Variation
Statisticians classify variation as
coming from either normal or special
causes
Phone calls
Instant messages
Lightning strikes
In-person interruptions
Normal and Special Cause
Variation
Vendor Bid Analysis
Use to determine whether price is
reasonable
Assume the lowest responsible offer is
fair
Prices may be determined in the
marketplace
Develop a “should cost estimate”
Value Engineering
Double-checking all of the chosen
methods
A separate stage may be incorporated
late in the project planning to ensure
time is spent on value engineering
Value engineering – “an approach used to optimize project life
cycle costs, save time, increase profits, improve quality, expand
market share solve problems and/or use resources more effectively."
Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
More involved methods for allocating
indirect costs
Yields more accurate cost information
Cost Drivers:
Number of
units produced
Number of
product
variations
Number of batches run
Amount of
facility utilized
Life Cycle Costing
The total costs of creating and using
the project during its useful life
Consider disposition costs of the
product after its useful life is complete
Time Value of Money
Discount the value of future revenue
and cost streams
Discount future dollars by the
appropriate factor
The finance department may provide
the appropriate rate
The rate depends on inflation rate plus
the cost of capital
Determine Budget
Aggregating costs
Analyzing reserve needs
Determining cash flow
Determine budget – “the process of aggregating the estimated
costs of individual activities or work packages to establish an
authorized cost baseline.”
Aggregating Costs
Direct and indirect costs add up to the
cost baseline
Cost performance baseline – “the approved version of
the time-phased project budget, excluding any
management reserves, which can be changed only
through formal change control procedures and is used as
a basis for comparing actual results.”
Aggregation of Project Budget
Analyzing Reserve Needs
Contingency reserve (risk analysis)
Management reserve (uncertainty)
Determining Cash Flow
Expenses are applied to individual
activities
Revenue tracked for availability
Cash from organization budgets on a
periodic basis
Cumulative cash >= demands?
Project Cumulative Cash and
Revenue
Establishing Cost Control
Budget baseline for project control
Milestones measuring point
◦ Milestone schedule - project charter
◦ Identified in constructing the project
schedule
Cash flow projections expected funding
Control cost – “the process of monitoring the status of
the project to update the project costs and managing
changes to the cost baseline.”
the project to update the project costs and managing
changes to the cost baseline.”
Using MS Project for Project
Budgets
Develop Bottom-Up Project Budget◦ Assignment costs
◦ Activity costs
◦ Project total costs
◦ Perspectives to view costs
Develop Summary Project Budget
Assignment Costs
Required data◦ Assignment work hours
◦ Resource Standard Rate
◦ Resource Overtime Rate
Activity Costs
Task Usage View with
Resource Work Form
Various Perspectives
Resource Usage view
◦ Assignment costs are summarized at the
resource level
Resource Usage View
Develop Summary Project
Budget
Add a dummy activity under each phasesummary
Estimate phase duration and the phase
cost
Duration estimate dummy activity’s
duration field
Cost estimate dummy activity’s Cost field
Remove each dummy activity when detail
is added
Dummy Activity for Late
Phase
Summary
The cost management plan outlineshow to structure and control project
costs
Cost estimating can be challenging
because of activity variation
Many methods are available to assist
in cost estimating.
Cost budgeting
◦ Aggregating individual costs
◦ Analyzing needs for cost reserves
◦ Determining cash inflow and outflow.
Establishing cost controls includes
establishing cost reporting systems.
MS Project can assist in developing
either bottom-up project budgets or
summary project budgets.
The Value of Budget
Optimization
A three PM IN ACTIONthree-year capital project portfolio is
developed for implementation and
budgeted.
Budgeting process conducted year round to balance multiple competing
objectives
Utility adopted a project portfolio
optimization process to create,
analyze. refine the budget for the refine the budget for the portfolio.
The electric utility adopted a project
portfolio optimization process
A computer-based mathematical
algorithm is used to optimize all
possible spending portfolios to
maximize value and minimize risk at
specified budget levels