allforquiz2
Scope Planning
Web Intelligence Solutions from Tera data
"An effective scope management approach fosters open communications and sound decision making to ensure all parties get business value expected from the project"
- Describe how to collect requirements
- Define scope processes.
- Create a requirements trace-ability matrix, project scope statement, and change request form.
- Describe a work breakdown structure (WBS) is
- Compare/contrast methods of developing a WBS.
- Create a WBS for a project
- Set up a WBS in MS Project
Scope Planning Processes
- Collect project requirements
- Define project's scope
- Create a work breakdown structure (WBS)
- Establish change control
Flow of Scope Planning
Plan Scope Management
Plan Scope Management - "the process of creating a scope management plan that documents how the project will be define, validated, and controlled." PMBOK GUIDE
- Total scope = product scope + project scope
Project scope - "the features and functions that characterize a product, service, or result." PMBOK Guide
- Identify and organize all project work
Project scope - "the work performed to deliver a product, service, or result with the specified features and functions." PMBOK Guide
Collect Requirements
- Make sure the project team is absolutely clear on the project objectives
Collect requirements - "the process of defining, documenting, and managing stakeholder needs and requirements to meet project objectives." PMBOK Guide
Gather Stakeholder Input
- Use voice of the customer techniques (VOC)
- Ask questions
- Place yourself in the customer's situation
- State customer desires in operational terms
- Seek a high-level description
What do we not understand about the request?
What is the business reason for the request?
What is the impact of not providing this feature?
What action items need to be accomplished if we do this?
What impact will this have on other parts of the project or elsewhere?
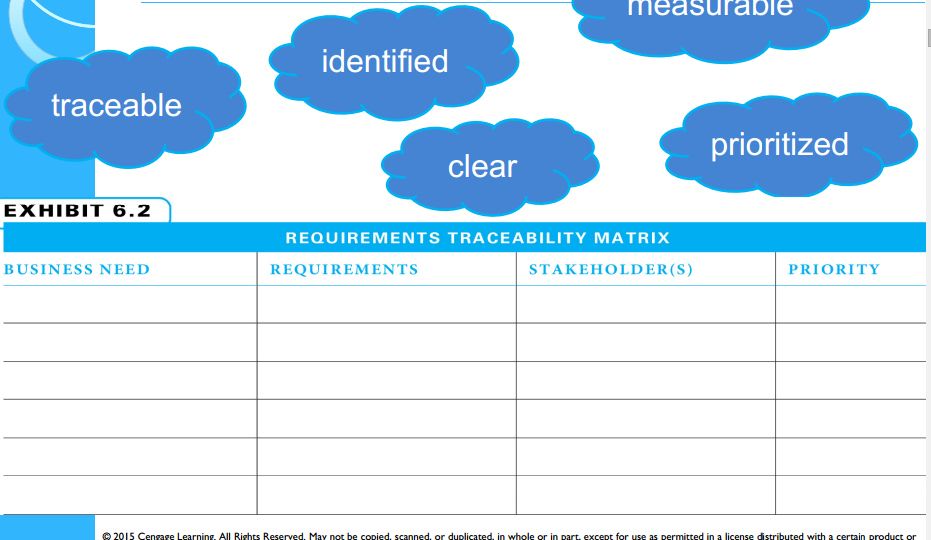
Requirements Trace-ability Matrix
-traceable
-identified
-clear-
-measurable
-prioritized
Define Scope
Define scope - "the process of developing a detailed description of the project and product." PMBOK Guide
- Reasons to Define Scope
- How to Define Scope
- List deliverable and acceptance criteria
- Establish project boundaries
- Create a project work statement
- How to Define Scope in Agile Projects
Reasons to Define Scope
How to Define scope
- List project deliverable
- Determine acceptance criteria
- Establish project boundaries
- In scope
- Out of scope
- Understand constraints
- Create a Scope Definition
How to Define Scope in Agile Projects
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- What is the WBS?
- Why use a WBS?
- WBS Formats
- Work Packages
- How to Construct a WBS
What is the WBS?
- A tool used to divide project deliverable into smaller pieces
- Identify deliverables
- A framework for further planning, execution, and control
Define activity - "the process of identifying the specific actions to be performed to produce the project deliverables" PMBOK GUIDE
Why use WBS?
- Adds discipline and visibility to project planning
- basic for planning schedule, resources, cost, quality, and risk
- Useful in determining where and why problems occur
- Helpful in project communications
WBS Formats
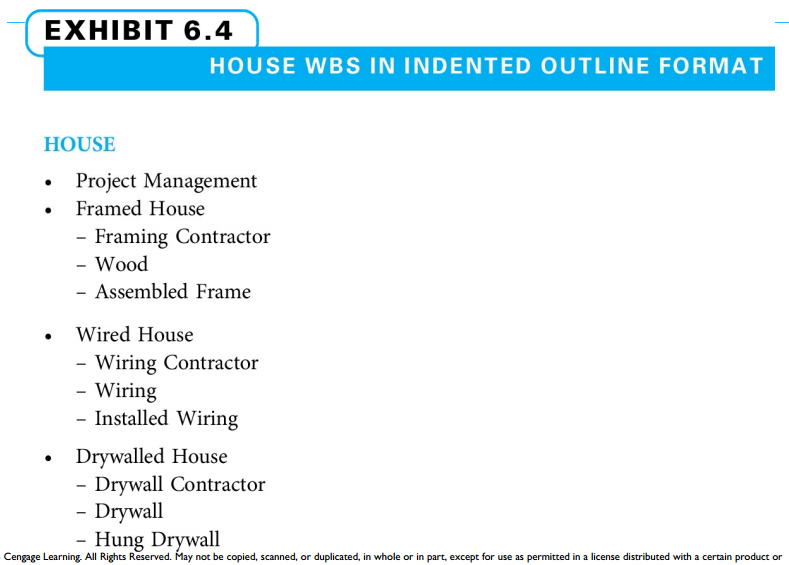
- Indented outline
- Organizational chart
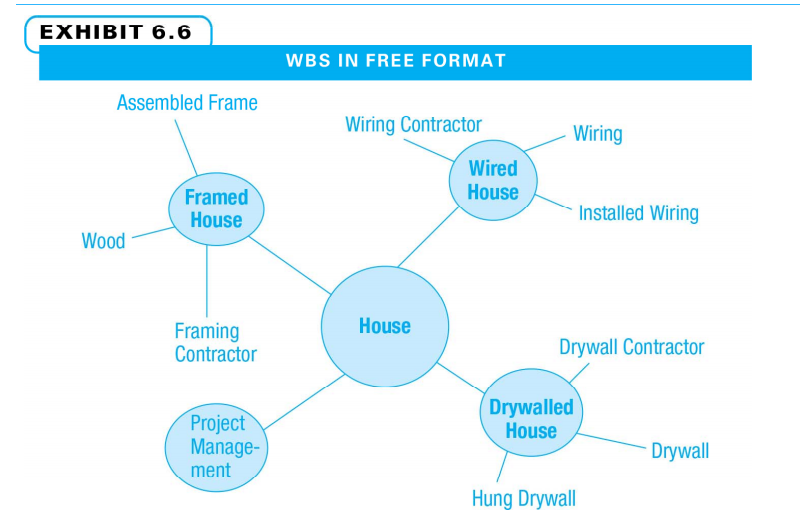
- Free format
WBS - Indented Outline Format
WBS in Org Chart Format
WBS in Free Format
Work Packages
- Lowest level element
- Basis for subsequent planning and control
work activities are defined
Schedule is formed
Resources are aligned
Control features are developed
Work packages - "the work defined at the lowest level of the work breakdown structure for which cost and duration can be estimated and managed." PMBOK Guide
Work Packages
- State succinctly in very few words
WBS component - "an entry in the WBS that can be at any level." PMBOK Guide
WBS dictionary - " a document that provides detailed deliverable, activity, and scheduling information about each component in the WBS." PMBOK Guide
Work Package Detail
How to construct a WBS
- Include a subject matter expert (SME)
- Use a top down approach
- Consider WBS from a previous project as a starting point
- Use brainstorming
Steps in WBS Construction
- Identify major deliverables
- Divide into smaller deliverables
- Continue until deliverables are the right size
- Review
Identify Major Deliverables
- Organize by project phase
- Facilitates rolling wave planning
- Rolling wave planning --> quick start
- Helps avoid:
- Analysis paralysis - never starting anything because the plan is not complete
- Ready, fire, aim - not planning at all
Rolling wave planning - "an iterative planning technque in which the work to be accomplished in the near term is planned in detail, while the work in the future is planned at a higher level." PMBOK Guide
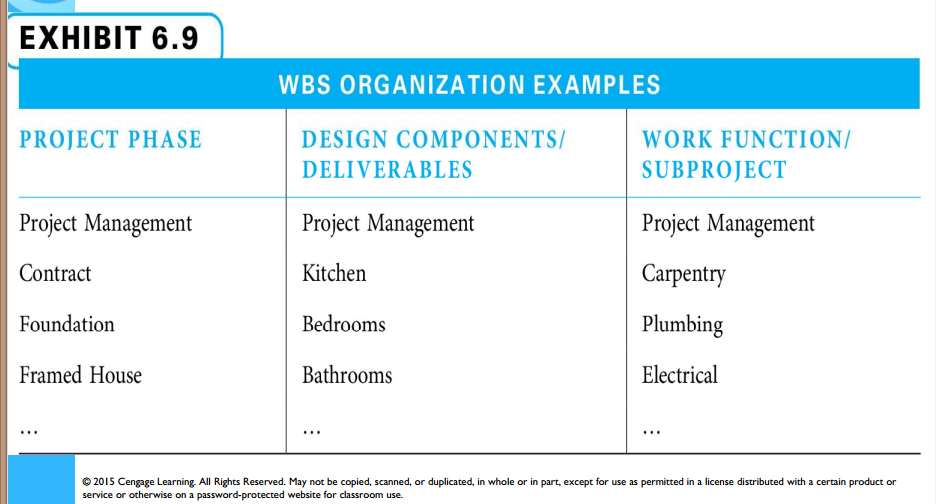
WBS Organization Examples
Work Function Organization
- Allows functions to focus on specific activities
- Does not promote cross-functional discussion
- Extra care required to establish inter-functional communication
Decompose deliverables
- Brainstorm a list of interim and final deliverables (use Post It Notes)
- Assemble deliverables on a large work space
- Group deliverables into related groups
Decomposition = "a technique for dividing and subdividing the project scope and project deliverables into smaller more manageable parts." PMBOK guide
Continue Until deliverables are the right size
Review
- Consider the parent-child concept
- Have between 3 and 9 child elements for each parent
- Uniquely name each component in the WBS
- Assign a unique number to each component
Establish Change Control
- Projects are conducted in an atmosphere of uncertainty
- Plans must be made for dealing with change
Change control
system - "approved set of procedures that describes how modifications to the project deliveraables and documentation will be managed and controlled." PMBOK Guide
Baseline - "the approved version of a work product that can be changed only through formal change control procedures and is used as a basis for comparision." PMBOK Guide
- Document potential changes to a project with a change request
- Every change to a project must be formally proposed
Change request - "a formal proposal to modify any document, deliverable, or baseline." PMBOK Guide
Change request Form
Using MS Project for Work Breakdown Structures (WBS)
- Set Up the WBS
Understand WBS definitions and displays.
Enter summaries.
Create the outline for your WBS. Insert row number column.
Hide (or show) the desired amount of detail.
Step 1. Understand WBS displays and definition
Step 2. Enter WBS Elements (Summaries)
Step 3. Create the Outline for your (WBS)
Step 4. Insert Row Number Column
- Project will automatically number summaries
- Right-click the Task Name heading
- Insert - Column - WBS
Ready to Insert WBS Column
WBS Column Inserted
Step 5. Hide (or Show) Underlying Detail
Summary
- Use scope planning to determine interim deliverables and work to perform
- Organize scope into work breakdown structure (WBS).
- Decompose the project into smaller and smaller pieces.
- Assign WBS components
- Create the project by hand or use MS Project to create the WBS
Work Breakdown Structure Template
- Management and Technical activities for banks in South Africa
Scheduling Projects
Web-based software implementations
"Establishing scope that can be accomplished in a 30 - to 60-day schedule helps our clients get started using their web-based applications faster..Project planning for the future becomes more realistic, improving the odds of success.
- Describe project schedule limitations and how to deal with them
- Describe potential problems in estimating time accurately and how to overcome them
- Use the activity on node (AON) method to develop a project schedule.
- Describe project schedule limitations and how to deal with them
- Describe potential problems in estimating time accurately and how to overcome them
- Use the activity on node (AON) method to develop a project schedule
- Describe how to adjust a project's sequence logic
- Identify the critical path using prescribed methods
- Depict a project schedule
Plan Schedule Management
Plan Schedule Management
Project time management processes
- Plan schedule management
- Define activities
- Sequence activities
- Estimate activity resources
- Estimate activity duration
- Develop schedule
- Control schedule
Adapted from PMBOK guide
Purposes of a Project Schedule
What is the earliest a particular activity can start, and when will it end?
What activity must begin before which other activities can take place?
When will the project be complete?
What would happen if a delivery of material was one week late?
Can a key worker take week vacation the first week of march?
If one worker is assigned to do two activities, which one must go first?
How many hours do we need from each worker next week or month?
Which worker or other resource is a bottle neck, limiting the speed of our project?
What will the impact be if the client wants to add another module?
If I am willing to spend an extra $10,000, how much faster can the project be completed?
Are all of the activities completed that should be by now?
Historical Development of Project Schedules
- Scheduling as a result of competition
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and Critical Path Method (CPM) – 1 950s
- Identify activities
- Determine their logical order
- Estimate the duration of each activity
Critical Path Method (CPM) – “a method used to estimate the
minimum project duration and determine the amount of scheduling flexibility on the logical network paths within the schedule model." PMBOK Guide
PERT
- Estimate most likely time needed to complete a project
- Estimate level of confidence in completing a project in a particular time
- Useful in (R&D) projects
DEPARTMENT OF THE
NAVY POLARIS
WEAPONS SYSTEM
CPM
DUPONT
ENGINEERING
SERVICES
DIVISION
- Used to plan very large projects
- Used single time estimates for Used single time estimates for each activity
- Focus on longest sequence of Focus on longest sequence of activities
- Used to determine how to complete a project early
- Useful in the construction industry
Activity Activity () on Node on Node (AON) or Precedence or Precedence
Diagramming Method (PDM)
Precedence Diagramming Method (PDM) – “a technique in which
the scheduled activities are represented by nodes and are graphically
linked by one or more logical relationships to show the sequence in by one or more logical relationships to show the sequence in
which the activities are performed” PMBOK® Guide
5 Factors Limit Project Completion
- Logical order in which activities need to be completed to be completed
- How long each activity will take
- How many key resources are available at specific points in the project
- Imposed dates Imposed dates
- Cash flow
Creation of Project Schedules
- Identify all activities
- Determine logical order Determine logical order
- Assign resources to each activity
- Estimate time required for that activity
- Compare schedule with imposed Compare schedule with imposed dates
- Consider project budget and cash Consider project budget and cash flow, quality demands, and risk factors
The Project Manager’s Responsibility
- Resist pressure to dictate a schedule
- Determine a schedule that is possible Determine a schedule that is possible
- Persuade stakeholders that the scheduled make sense
- Deliver the project according to the agreed-upon schedule
Define Activities
- WBS with WBS with deliverables only
- Don’t omit activities
- Activity sequencing may uncover Activity sequencing may uncover missing activities
- The schedule will not be approved until all related planning is in place
- Avoid adding activities after the final schedule is approved
- Use previous projects, templates, or checklists as a starting point checklists as a starting point
List Project Milestones List Project Milestones
- Completion of a major deliverable
- Completion of a critical activity
- Prior to a large financial commitment
- Merging point in the project schedule